The Strategic Role of GCCs as Engineering Hubs in Global Growth

In today’s evolving technological landscape, the concept of Gccs as Engineering Hubs is gaining significant attention. These centers are becoming the backbone of innovation and technical excellence by bringing together skilled engineers, advanced technologies, and streamlined processes. By focusing on specialized engineering tasks, GCCs as Engineering Hubs help organizations to centralize operations, enhance technical expertise, and drive cost efficiency. Their strategic locations and focus on talent development allow them to offer valuable support to global engineering functions, shaping the future of product design, system development, and infrastructure optimization.
The Strategic Importance of GCCs as Engineering Hubs
The emergence of Gccs as Engineering Hubs plays a critical role in supporting global engineering demands. These hubs serve as centralized units where engineering solutions are designed, tested, and optimized for global deployment. By operating as technical centers of excellence, GCCs as Engineering Hubs align closely with core business goals and innovation strategies. Their contribution goes beyond basic support, driving meaningful advancements in design automation, process improvement, and product scalability. They also foster an environment where engineers can collaborate across geographies, leveraging diverse ideas to solve complex engineering challenges efficiently and creatively.
Advancing Talent Development in GCCs as Engineering Hubs
One of the essential components of Gccs as Engineering Hubs is their focus on building and nurturing engineering talent. These hubs provide an ideal platform for skilled professionals to develop expertise in areas such as software engineering, mechanical design, electronics, and system integration. GCCs as Engineering Hubs also encourage a culture of learning and continuous improvement, where engineers are empowered to upgrade their skills, explore emerging technologies, and innovate in their respective fields. This commitment to talent development not only strengthens the engineering function but also ensures the hub's long-term sustainability and growth in a highly competitive global market.
Driving Technological Innovation through GCCs as Engineering Hubs
The impact of Gccs as Engineering Hubs extends deeply into technological innovation. These hubs act as key drivers of new product development and digital transformation initiatives by creating solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce time to market, and improve product quality. GCCs as Engineering Hubs also leverage modern technologies such as artificial intelligence, automation, and cloud computing to optimize engineering processes. Their ability to adapt to rapid technological changes and integrate cutting-edge tools into existing workflows helps organizations maintain a competitive edge. Through focused innovation efforts, these hubs contribute to the creation of next-generation products and solutions.
The Future Outlook for GCCs as Engineering Hubs
The future of Gccs as Engineering Hubs looks promising as global industries continue to rely on specialized engineering expertise for sustainable growth. With the increasing demand for digital products, smart manufacturing solutions, and innovative infrastructure, GCCs as Engineering Hubs are well-positioned to lead the next wave of engineering transformation. These hubs will likely expand their capabilities in areas like robotics, renewable energy, and advanced analytics to support future engineering needs. By continuously evolving their strategies and building strong talent pools, GCCs as Engineering Hubs will remain central to global engineering success, driving both technological and economic progress in the years to come.
Gccs as Engineering Hubs represent a powerful combination of talent, technology, and strategy. As they continue to evolve, these hubs will play a vital role in shaping the future of engineering and innovation across industries worldwide.
Categories
Read More
Soft clay, or 輕黏土, is an air-dry modeling material known for its light weight, smooth texture, and versatility. It has gained popularity among educators, hobbyists, and professional artists for both educational and decorative purposes. Composition and BenefitsUnlike traditional clay, soft clay is air-drying, non-toxic, and mess-free. It allows for intricate detail and vibrant colors without the...

"Executive Summary Flavoured Snack Pellets Market : Flavoured snack pellets market is expected to be growing at a growth rate of 4.90% in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028. The growing hectic lifestyle will act as a driving factor to the growth of the flavoured snack pellets market. As it is important to have valuable and actionable market insights for creating sustainable and...

Executive Summary Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Market : CAGR Value The global emergency medical services (EMS) market size was valued at USD 50.54 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 98.51 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.70% during the forecast period The data and information about industry are taken from reliable sources such as...

"Executive Summary Coronary Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) Market : CAGR Value The global coronary intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) market size was valued at USD 277.94 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 493.50 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.44% during the forecast period Coronary Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) Market report makes...

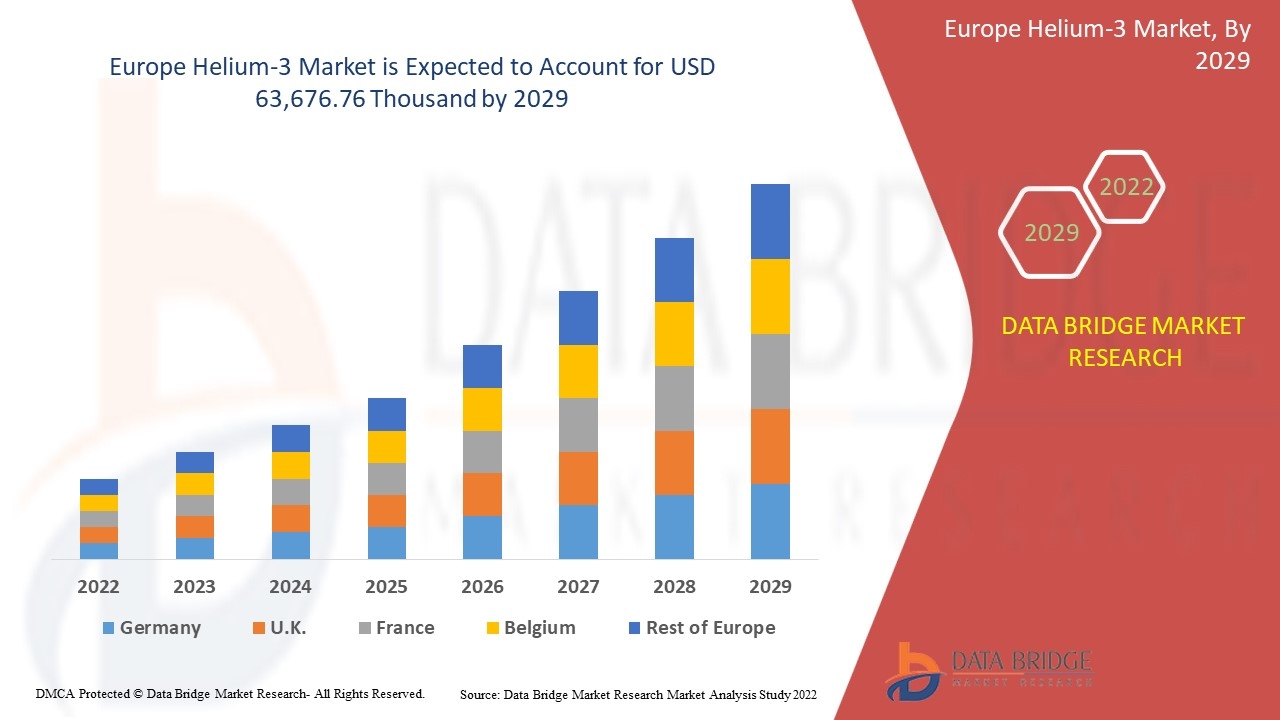
Executive Summary Helium 3 Market : The global helium 3 market size was valued at USD 178.68 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 224.59 million by 2031, with a CAGR of 2.9% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2031. CAGR Value Helium 3 Market research report is generated with the best and advanced tools of collecting, recording, estimating and analysing market data....